Last Updated on September 30, 2022
The decline triceps extension with dumbbells is an effective isolation exercise designed to target the triceps muscles, specifically the long head. By incorporating the decline bench, this movement increases the challenge, forcing the triceps to work harder than they would on a flat bench. The decline position shifts more resistance onto the triceps, making this exercise one of the best choices for developing arm strength and muscle definition.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover the benefits of the decline triceps extension, how to perform it with proper form, common mistakes to avoid, and how to integrate it into your workout routine for optimal triceps development.
What Is the Decline Triceps Extension with Dumbbells?
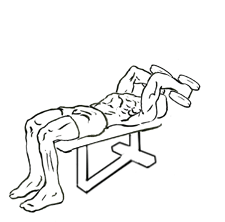
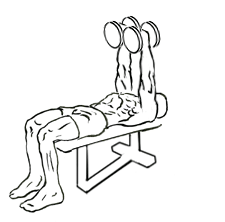
The decline triceps extension with dumbbells is a variation of the classic triceps extension, also known as a “skull crusher.” By using a decline bench, this version places more emphasis on the triceps’ long head, making it a more intense workout for your upper arms. The exercise involves extending your arms while holding dumbbells, lowering the weights behind your head, and then pressing them back up to the starting position.
This movement isolates the triceps, reducing the involvement of other muscle groups, which ensures a more concentrated workout that targets the triceps brachii—the muscle responsible for elbow extension and arm stabilization. If your goal is to build stronger and more defined arms, this exercise is a great addition to your routine.
Muscles Worked in the Decline Triceps Extension with Dumbbells
The decline triceps extension primarily targets the triceps brachii but also engages supporting muscles for stability:
- Triceps Brachii: This is the primary muscle worked during the exercise. The triceps consist of three heads—the long head, lateral head, and medial head. The decline angle emphasizes the long head, which contributes to overall arm mass and strength.
- Anterior Deltoids (Shoulders): The front part of your shoulders assists in stabilizing the arms throughout the movement, though they are not the primary focus.
- Forearms: The forearm muscles are engaged to help stabilize and control the dumbbells as you lower and lift them.
- Core Muscles: Since the exercise is performed on a decline bench, your core is also engaged to stabilize your body and maintain proper posture during the movement.
Benefits of the Decline Triceps Extension with Dumbbells
Adding the decline triceps extension with dumbbells to your workout routine offers a range of benefits that can enhance both arm strength and overall upper body development:
- Isolated Triceps Engagement: This exercise specifically targets the triceps without involving too many other muscle groups. The decline position adds intensity, leading to better muscle activation and growth.
- Increased Range of Motion: Using dumbbells allows for a greater range of motion compared to a barbell, providing a deeper stretch in the triceps and promoting better flexibility and muscle development.
- Improved Arm Strength: Consistently performing decline triceps extensions helps increase triceps strength, which in turn supports other pressing exercises such as the bench press and overhead press.
- Balanced Arm Development: Since each arm works independently when using dumbbells, this exercise helps correct any muscle imbalances that can occur with bilateral exercises.
- Reduced Joint Stress: Dumbbells allow for a more natural movement path, reducing the stress on your elbows and wrists that can occur with other triceps exercises, such as barbell skull crushers.
- Enhanced Arm Definition: Targeting the triceps helps improve arm definition and shape. The triceps make up a large portion of your upper arm, so strengthening them is key to achieving a well-toned appearance.
Proper Technique for Decline Triceps Extension with Dumbbells
To maximize the benefits of the decline triceps extension with dumbbells and minimize the risk of injury, it’s important to perform the exercise with proper form. Follow these step-by-step instructions for optimal results:
- Set up the decline bench: Adjust the bench to a decline angle, usually between 15 to 30 degrees. Sit on the bench and secure your feet under the footpads to keep yourself stable during the exercise.
- Grab the dumbbells: Select a pair of dumbbells that you can control throughout the exercise. Lie back on the bench with a dumbbell in each hand and your arms extended above your chest, palms facing each other. This is your starting position.
- Position your arms: Your arms should be fully extended but with a slight bend in your elbows to avoid locking the joints. Keep your elbows stationary throughout the movement—only your forearms should move.
- Lower the dumbbells: Slowly lower the dumbbells in an arc toward your head, bending at the elbows. The goal is to lower the dumbbells until they are near your head or just behind it. Focus on maintaining control and not letting the weights drop too quickly.
- Engage your triceps: Once the dumbbells are near your head, pause briefly to feel the stretch in your triceps. Then, using your triceps, press the dumbbells back up to the starting position. Ensure that you fully extend your arms without locking your elbows.
- Repeat: Perform the desired number of repetitions, typically 3 to 4 sets of 8 to 12 reps, depending on your fitness goals. Maintain a slow and controlled movement throughout the exercise to ensure proper muscle engagement.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To get the most out of the decline triceps extension with dumbbells and prevent injury, avoid these common mistakes:
- Flaring the Elbows: Allowing your elbows to flare out too much can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and shift the focus away from the triceps. Keep your elbows close to your head throughout the movement.
- Using Too Much Weight: Lifting weights that are too heavy can lead to poor form, such as swinging the dumbbells or relying on momentum. Choose a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with control and proper technique.
- Locking the Elbows: Locking your elbows at the top of the movement takes the tension off your triceps and can lead to joint strain. Keep a slight bend in your elbows to maintain continuous tension in your triceps.
- Not Controlling the Descent: Letting the dumbbells drop too quickly reduces time under tension, which is essential for muscle growth. Focus on a slow and controlled descent to maximize the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Arching the Back: To prevent lower back strain, keep your core engaged and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement. Avoid excessive arching of your lower back while lying on the decline bench.
Variations of the Decline Triceps Extension with Dumbbells
Once you’ve mastered the standard decline triceps extension with dumbbells, try incorporating these variations to add variety and challenge to your workout routine:
- Single-Arm Decline Triceps Extension: Perform the exercise one arm at a time to isolate each triceps muscle more effectively. This variation helps correct muscle imbalances and improves unilateral strength.
- Decline Barbell Triceps Extension: Use a barbell or EZ bar instead of dumbbells for a different variation. The barbell allows for heavier weights, which can increase the intensity of the exercise.
- Incline Triceps Extension: Perform the same movement on an incline bench to target the triceps from a different angle. This variation emphasizes the upper portion of the triceps.
- Flat Bench Triceps Extension: Use a flat bench to perform the exercise. This variation reduces the intensity compared to the decline version but still provides an effective triceps workout.
- Overhead Dumbbell Triceps Extension: Perform the exercise while sitting or standing, with the dumbbells lifted overhead. This variation provides a different angle for targeting the triceps, engaging the entire muscle group.
How to Incorporate Decline Triceps Extension with Dumbbells into Your Workout Routine
The decline triceps extension with dumbbells can be integrated into a variety of upper body or arm-focused workout routines. Here’s how to effectively incorporate it into your program:
- Frequency: Aim to perform this exercise 1 to 2 times per week, depending on your training split. It works well as part of an arm day or as a secondary movement on a chest or push day.
- Reps and Sets: For muscle growth, perform 3 to 4 sets of 8 to 12 reps. For strength, opt for 4 to 5 sets of 4 to 6 reps with heavier weights.
- Combine with Other Triceps Exercises: Pair the decline triceps extension with other triceps movements, such as close-grip bench presses, dips, or cable pushdowns, for a complete triceps workout.
- Rest Between Sets: Allow 60 to 90 seconds of rest between sets to give your muscles time to recover while maintaining intensity.
Sample Arm Workout with Decline Triceps Extension
Here’s a sample workout that incorporates the decline triceps extension into a full arm routine:
- Close-Grip Bench Press – 4 sets of 8-10 reps
- Decline Dumbbell Triceps Extension – 4 sets of 8-12 reps
- Cable Triceps Pushdown – 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Triceps Dips (Bodyweight or Weighted) – 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Overhead Dumbbell Triceps Extension – 3 sets of 10-12 reps
Final Tips for Success
- Prioritize Form Over Weight: It’s essential to focus on proper form before increasing the weight. Start with lighter dumbbells to ensure you’re controlling the movement and engaging your triceps effectively. As you build strength, gradually increase the weight for a more challenging workout.
- Engage Your Core: Since this exercise is performed on a decline bench, it’s important to keep your core engaged to stabilize your body. This will help prevent lower back strain and ensure that you maintain proper posture throughout the movement.
- Use a Spotter for Heavy Lifting: If you’re lifting heavier weights or pushing yourself close to failure, consider having a spotter present to assist you if needed. A spotter can help ensure your safety, especially during the lowering phase of the exercise.
- Progress Gradually: To see continuous gains, progressively overload the triceps by increasing the weight or reps over time. This will keep your muscles challenged and ensure steady progress.
- Combine with Compound Movements: While the decline triceps extension is a great isolation exercise, it works best when paired with compound movements such as close-grip bench presses or dips to target the entire triceps muscle.
- Stay Consistent: Like any other strength-building exercise, consistency is key to seeing results. Make the decline triceps extension a regular part of your arm workout routine to achieve stronger, more defined triceps over time.
The decline triceps extension with dumbbells is a powerful exercise that delivers impressive results for anyone looking to enhance their arm strength and definition. By using dumbbells and the decline bench, this exercise provides a challenging and effective way to target the triceps while also engaging other stabilizing muscles. Whether you’re a beginner looking to strengthen your upper body or an experienced lifter aiming to refine your arm training, this exercise should be a key part of your routine.
Incorporate it into your workout plan, focus on proper form, and gradually increase the intensity to unlock the full potential of your triceps. With dedication and consistency, the decline triceps extension with dumbbells will help you achieve the toned, strong arms you’ve been working toward.
Exercise images by Everkinetic.






