Last Updated on September 30, 2014
The Exercise Ball Pull-In is a dynamic and effective movement that specifically targets the lower abdominal muscles while also engaging other stabilizing muscles in the core, shoulders, and legs. This exercise utilizes an exercise ball, also known as a stability ball, to add an extra element of instability, forcing your body to work harder to maintain balance and control. By incorporating the Exercise Ball Pull-In into your core routine, you can strengthen your abs, improve balance, and develop greater core stability, which is essential for overall functional fitness.
In this guide, we’ll take an in-depth look at the Exercise Ball Pull-In—discussing how it works, the benefits it provides, step-by-step instructions, common mistakes to avoid, and how to incorporate it into your workout routine. Let’s get started on your path to a stronger core and more defined lower abs.
Why the Exercise Ball Pull-In?
The Exercise Ball Pull-In is a powerful exercise for several reasons. Not only does it focus on the lower abdominal muscles, which are often neglected in traditional ab exercises, but it also engages the entire core, including the obliques and rectus abdominis, as well as the shoulders and hip flexors. The use of a stability ball introduces an additional challenge, as it forces you to balance while performing the movement, leading to greater muscle activation and improved core strength.
Here are some key reasons why this exercise should be part of your core training:
- Targets Lower Abdominal Muscles: One of the main reasons people struggle with lower abdominal exercises is because it’s difficult to isolate this muscle group. The Exercise Ball Pull-In specifically targets the lower abs, helping to strengthen and tone this area.
- Engages the Entire Core: While the focus is on the lower abs, the entire core—including the upper abs, obliques, and deep stabilizing muscles—works to keep your body balanced and stable on the exercise ball.
- Improves Balance and Stability: Because you’re supporting yourself with your hands while balancing your feet on an unstable surface, this exercise forces you to engage stabilizing muscles that aren’t usually activated in traditional ab exercises like crunches or sit-ups.
- Strengthens the Shoulders and Arms: In addition to working your abs, this movement requires you to support your body weight with your arms and shoulders, making it an effective upper body strengthening exercise as well.
- Increases Functional Strength: This exercise mimics real-life movements that require core stability and coordination, such as lifting, pushing, and pulling. By strengthening your core through this exercise, you can improve your performance in everyday activities and sports.
- Versatile and Scalable: The Exercise Ball Pull-In can be easily modified to suit all fitness levels. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced athlete, you can adjust the difficulty of the exercise by using different ball sizes, changing the range of motion, or adding other variations to challenge yourself further.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Exercise Ball Pull-In
Equipment Needed:
- Exercise Ball (Stability Ball): Choose an exercise ball that suits your height. When sitting on it, your knees should form a 90-degree angle. Smaller balls make the exercise more challenging, while larger ones provide more stability.
Starting Position:
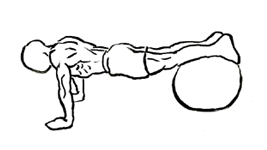
- Get Into a Push-Up Position: Begin by assuming a push-up or plank position with your arms extended and your hands shoulder-width apart on the floor. Your body should form a straight line from your head to your heels.
- Place Your Feet on the Ball: Carefully place your shins and the tops of your feet on the exercise ball. The ball should rest just below your knees, and your legs should be fully extended. Make sure your body remains in a straight line from your shoulders to your feet.
- Engage Your Core: Tighten your abdominal muscles to stabilize your body. It’s essential to keep your back flat and your core engaged throughout the movement to avoid straining your lower back.
The Movement:
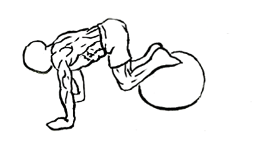
- Pull Your Knees Toward Your Chest: Begin the movement by pulling your knees toward your chest in a controlled manner. As your knees bend, the exercise ball will roll forward under your ankles. Focus on using your lower abdominal muscles to pull your legs in, and maintain a straight back throughout the movement.
- Crunch Your Abs at the Top: Once your knees are fully pulled in and the ball is under your feet, pause at the top and squeeze your abs. This contraction is what really activates the lower abdominal muscles, so hold the position for a brief moment to maximize the benefit.
- Roll the Ball Back: After pausing at the top, slowly straighten your legs and roll the ball back to the starting position. Make sure to control the movement as you return to the plank position, keeping your core tight and your back straight.
- Repeat: Perform the exercise for 10–15 repetitions, depending on your fitness level and the difficulty of the movement. Complete 3–4 sets for a thorough core workout.
Tips for Proper Form and Technique
To get the most out of the Exercise Ball Pull-In and avoid injury, it’s important to focus on proper form and technique. Here are some key tips to ensure you’re performing the exercise correctly:
- Keep Your Back Straight: Maintaining a neutral spine is crucial during this exercise. Avoid arching your back, as this can place unnecessary stress on your lower back and reduce the effectiveness of the movement. If you find your back sagging, it may indicate that your core isn’t fully engaged.
- Engage Your Core Throughout: Your core should remain tight and engaged throughout the entire movement, from the moment you start pulling your knees in to when you return to the starting position. This not only strengthens your abs but also protects your lower back.
- Control the Movement: Avoid using momentum to roll the ball in and out. The exercise should be performed in a slow and controlled manner, with a focus on using your abdominal muscles to drive the movement rather than relying on the ball’s momentum.
- Don’t Let Your Hips Drop: As you extend your legs back into the starting position, make sure your hips don’t drop. Keeping your hips in line with your shoulders helps maintain proper posture and ensures the exercise targets the correct muscles.
- Avoid Over-Rolling: While it’s important to bring your knees toward your chest, avoid over-rolling the ball to the point where your hips rise too high. This reduces the tension on your abs and shifts the focus to other muscles.
- Breathe Properly: Remember to breathe during the exercise. Inhale as you roll the ball forward, and exhale as you pull your knees in and squeeze your abs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Although the Exercise Ball Pull-In is simple in theory, there are a few common mistakes that can reduce its effectiveness or lead to injury:
- Arching Your Lower Back: One of the most common mistakes is allowing your lower back to arch as you roll the ball back. This often happens when the core isn’t engaged properly. To avoid this, focus on keeping your spine neutral and your core tight.
- Using Momentum: Some people rely on momentum to pull the ball in and out, rather than using their abdominal muscles. This can make the exercise less effective. Always perform the movement slowly and with control to ensure you’re targeting the right muscles.
- Dropping the Hips: When rolling the ball back to the starting position, it’s easy to let the hips drop too low, putting pressure on the lower back. Be mindful of your form and keep your hips in line with your body to prevent injury.
- Going Too Fast: Rushing through the exercise reduces muscle engagement and makes it harder to maintain proper form. Focus on slow, controlled movements to maximize the impact on your abs.
- Improper Ball Size: Using an exercise ball that is too large or too small can make the exercise more difficult or compromise your form. Choose the correct size for your height to ensure proper body alignment.
Variations and Modifications
The Exercise Ball Pull-In can be modified to suit different fitness levels or to add variety to your workout. Here are a few variations to try:
- Single-Leg Pull-In: For an extra challenge, perform the exercise with one leg on the ball while keeping the other leg extended in the air. This variation increases the difficulty by adding an additional element of balance and requires more core strength.
- Incline Pull-In: To make the exercise easier, you can perform it on an incline by placing your hands on a raised surface such as a bench or step. This reduces the amount of weight you have to support and makes the movement less challenging.
- Push-Up to Pull-In: For a more advanced variation, combine a push-up with the pull-in movement. After completing a push-up, immediately pull your knees toward your chest and roll the ball forward. This variation engages both your upper body and core for a more comprehensive workout.
- Stability Ball Mountain Climbers: In this variation, you alternate pulling one knee toward your chest at a time, simulating a mountain climbing motion. This adds a cardiovascular element to the exercise and increases core engagement.
- Medicine Ball Pass: Place a medicine ball between your feet as you perform the pull-in. When your knees are pulled in, pass the ball to your hands, and then extend your legs again. This variation adds an extra layer of challenge to your coordination and core strength.
How to Incorporate Exercise Ball Pull-Ins into Your Routine
The Exercise Ball Pull-In is a versatile movement that can be included in various types of workouts. Here’s how you can incorporate it into your routine:
- Core-Focused Days: On days when you’re focusing on building core strength, the Exercise Ball Pull-In can serve as one of your primary exercises. Pair it with other core movements like planks, leg raises, and Russian twists for a well-rounded abdominal workout. Aim for 3-4 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
- Full-Body Workouts: This exercise can be seamlessly integrated into a full-body workout routine, as it engages not only your abs but also your shoulders, arms, and even your legs to some extent. Use it in combination with exercises like squats, push-ups, and deadlifts to ensure you’re hitting all major muscle groups. This is particularly effective if you’re short on time and want to get the most out of your workout.
- As a Finisher: If you’ve just finished a strength-training session or a cardio workout and want to make sure your core is thoroughly worked, include Exercise Ball Pull-Ins as a finisher. It’s a great way to exhaust your core muscles and ensure that every part of your abs has been activated.
- Supersets and Circuits: To increase the intensity of your workout, consider adding Exercise Ball Pull-Ins into a superset or circuit. For example, you can alternate between this exercise and other core-focused movements, like bicycle crunches or mountain climbers, with minimal rest in between. This approach will challenge your endurance and keep your heart rate elevated, providing both strength and cardio benefits.
Sample Workout Routine Incorporating Exercise Ball Pull-Ins
Here’s an example of how you can include Exercise Ball Pull-Ins in a core workout:
- Warm-Up: 5-10 minutes of light cardio (e.g., jogging or cycling) and dynamic stretching.
- Plank with Shoulder Taps: 3 sets of 12 taps per side.
- Exercise Ball Pull-In: 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
- Bicycle Crunches: 3 sets of 20 reps (10 per side).
- Leg Raises: 3 sets of 12-15 reps.
- Russian Twists: 3 sets of 20 reps (10 per side).
- Cool Down: Static stretching focusing on the core and hip flexors.
This workout will help you build core strength and stability while also working your lower abs specifically through the Exercise Ball Pull-In.
Benefits of Regularly Performing Exercise Ball Pull-Ins
- Strengthens Lower Abs: The primary benefit of this exercise is the isolation and strengthening of the lower abdominal muscles, which are often difficult to target with traditional ab exercises.
- Improves Core Stability: The instability of the exercise ball forces your core muscles to engage more effectively, leading to greater overall stability and functional strength.
- Enhances Balance and Coordination: Because you’re balancing on the ball while performing the movement, your body’s proprioception (awareness of movement and body position) improves, which is helpful in both athletic performance and everyday tasks.
- Supports Better Posture: A strong core is essential for maintaining good posture, and regularly performing this exercise can help correct posture imbalances by strengthening the muscles that support your spine.
- Increases Functional Strength: The Exercise Ball Pull-In mimics real-life movements that require core engagement, such as lifting, bending, or reaching, making it a valuable exercise for improving functional fitness.
The Exercise Ball Pull-In is an essential movement for anyone looking to target their lower abs and build overall core strength. Its unique combination of abdominal engagement, balance, and stability makes it a highly effective exercise for improving both strength and functional fitness. By incorporating it into your regular workout routine, you’ll not only enhance your core muscles but also improve posture, balance, and coordination.
As with any exercise, proper form is crucial. Focus on maintaining a straight back, engaging your core throughout the movement, and controlling the motion of the ball. Avoid rushing through the exercise—quality over quantity will yield the best results.
Whether you’re a beginner working on foundational core strength or an advanced athlete seeking to challenge your stability, the Exercise Ball Pull-In is a valuable addition to your fitness arsenal. Include it in your next workout and start reaping the benefits of a stronger, more stable core!.