Last Updated on August 27, 2024
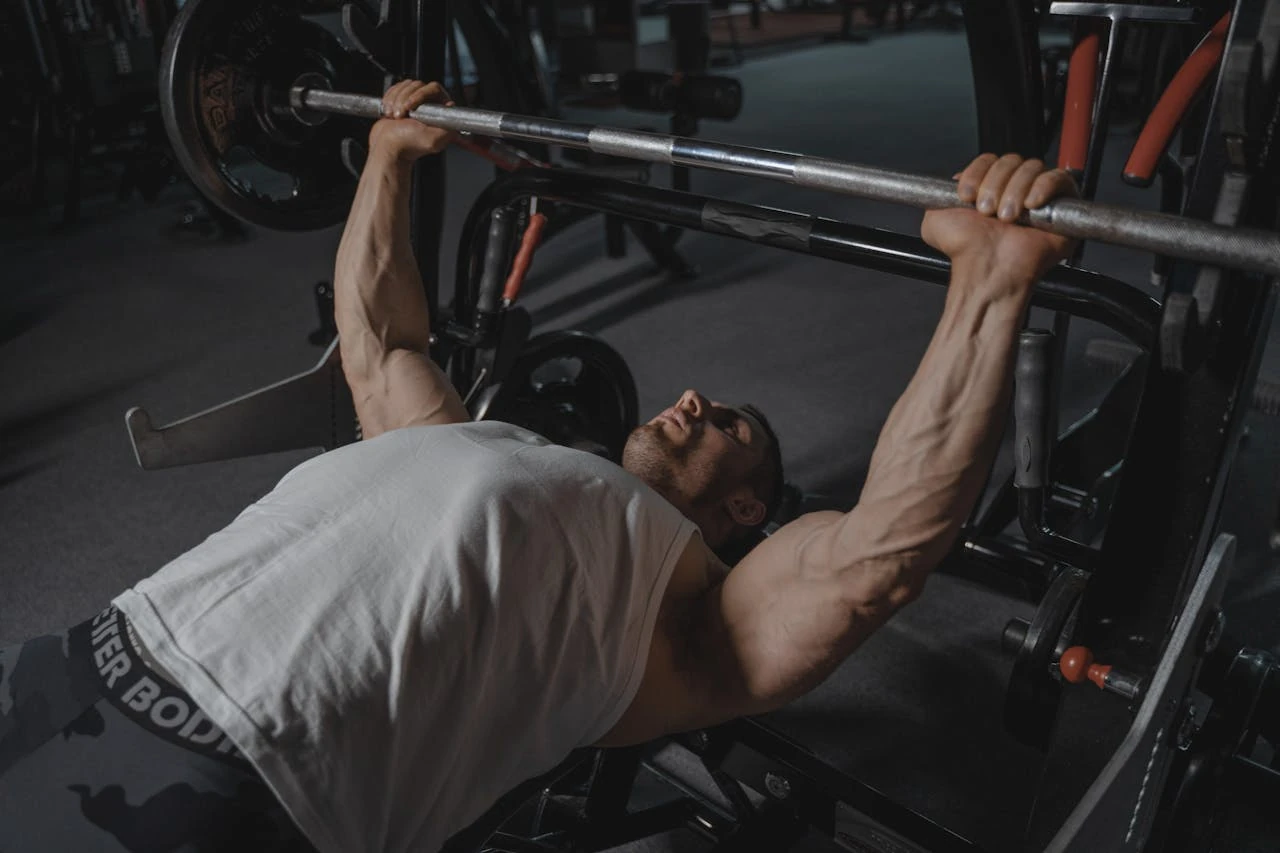
The bench press is a cornerstone exercise in strength training, renowned for its effectiveness in building a powerful chest. Whether you’re a seasoned lifter or a beginner just starting your fitness journey, understanding the nuances of the bench press can significantly enhance your workout routine. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the bench press, exploring everything from proper form and technique to tips for maximizing your gains.

Understanding the Bench Press
The bench press primarily targets the pectoral muscles, or chest muscles, but it also engages the shoulders and triceps. It’s a compound exercise, meaning it works multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making it an efficient choice for building upper body strength.
Benefits of the Bench Press
- Muscle Growth: The bench press is highly effective for hypertrophy, or muscle growth, particularly in the chest area.
- Strength Development: Regularly performing the bench press can increase overall upper body strength.
- Versatility: It can be modified in various ways to target different muscle groups or to accommodate different fitness levels.
- Functional Strength: The movement mimics many real-world pushing actions, enhancing functional strength.
Perfecting Your Bench Press Technique
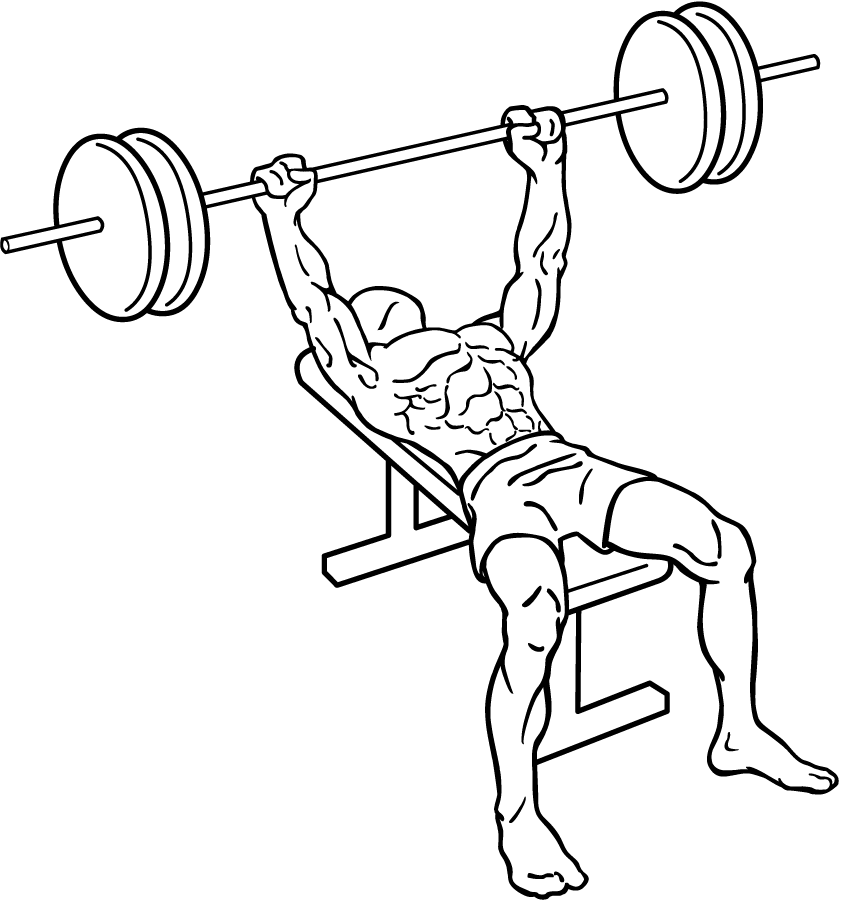
Executing the bench press with proper form is crucial not only for maximizing effectiveness but also for preventing injury. Here’s a step-by-step guide to mastering the bench press:
Step 1: Set Up Your Position
- Lie on a Flat Bench: Position yourself on a flat bench with your feet firmly planted on the floor. Your back should be flat against the bench, ensuring stability and support throughout the exercise.
- Grip the Bar: Grasp the barbell slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. This grip ensures optimal engagement of your chest muscles while maintaining control over the bar.
Step 2: Establish Your Starting Position
- Lift the Barbell: Raise the barbell above your body, aligning it over the middle of your chest. This position serves as your starting point.
- Engage Your Core: Tighten your core muscles to maintain stability and protect your lower back during the lift.
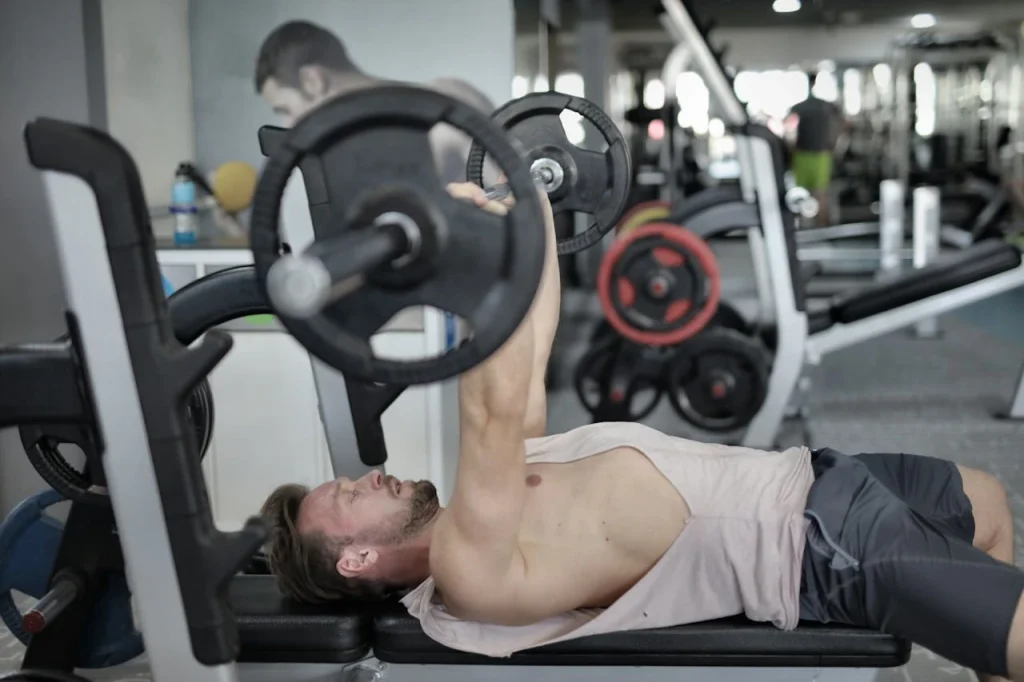
Step 3: Execute the Lift
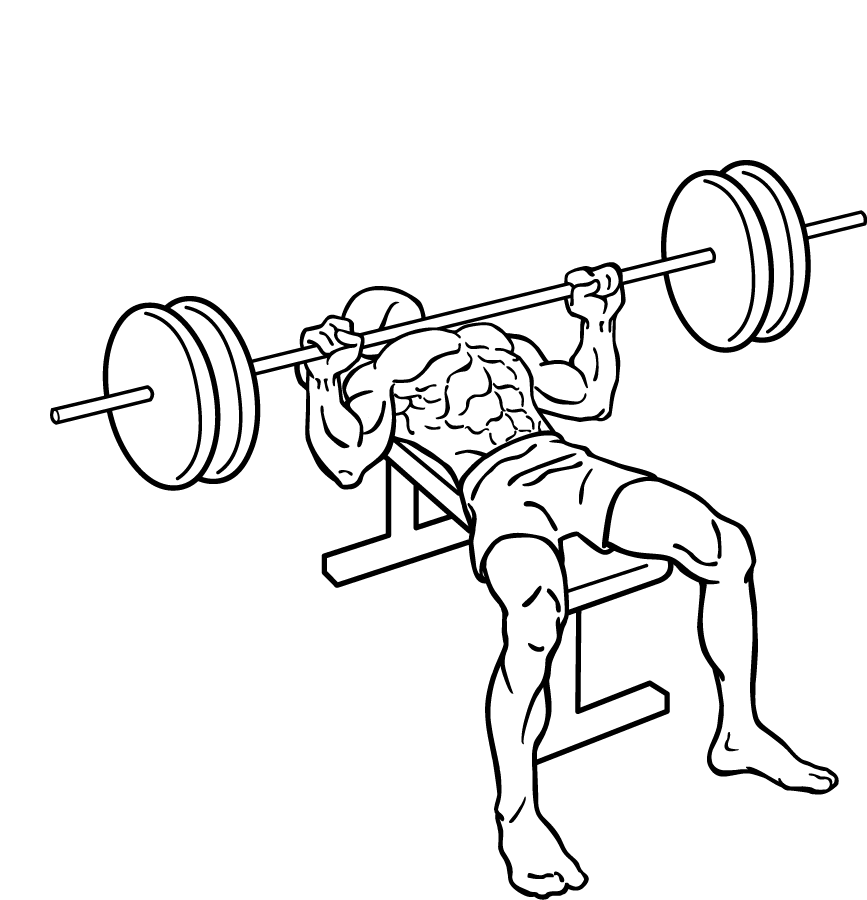
- Lower the Barbell: Gradually lower the barbell until it just touches your chest. This controlled descent is crucial for maintaining tension in your muscles and preventing injury.
- Press Upward: Push the barbell upward until your arms are fully extended and your elbows are locked. This movement should be powerful yet controlled.
Step 4: Return to Starting Position
- Controlled Descent: Lower the barbell back to its starting position over your chest with control.
- Repeat: Continue with additional repetitions as per your workout plan.
Tips for an Effective Bench Press
To get the most out of your bench press routine, consider these expert tips:
- Warm-Up Properly: Always start with a warm-up set using lighter weights to prepare your muscles and joints for heavier lifting.
- Focus on Breathing: Inhale as you lower the bar and exhale as you press it upward. Proper breathing helps maintain core stability and enhances performance.
- Use Spotters When Needed: If you’re lifting heavy weights, having a spotter can ensure safety and provide assistance if needed.
- Progress Gradually: Increase weights incrementally to avoid overloading your muscles too quickly, which can lead to injury.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even seasoned lifters can fall into bad habits when bench pressing. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Arching Your Back Excessively: While a slight arch is natural, excessive arching can strain your lower back.
- Bouncing the Bar Off Your Chest: This not only reduces effectiveness but also increases injury risk.
- Flared Elbows: Keep elbows at about a 45-degree angle from your body to reduce shoulder strain.
- Neglecting Leg Drive: Engaging your legs can provide additional stability and power during lifts.
Variations of the Bench Press
To keep your workouts dynamic and target different muscle groups, consider incorporating these variations:
- Incline Bench Press: Targets upper chest muscles more intensely by adjusting the bench to an inclined position.
- Decline Bench Press: Focuses on lower chest muscles by setting the bench at a decline.
- Dumbbell Bench Press: Enhances balance and coordination by using dumbbells instead of a barbell.
Incorporating Bench Press into Your Routine
For optimal results, integrate the bench press into a balanced workout regimen that includes exercises targeting all major muscle groups. Here’s an example of how you might structure a weekly workout plan:
- Day 1 (Chest and Triceps):
- Bench Press
- Incline Dumbbell Press
- Tricep Dips
- Push-Ups
- Day 2 (Back and Biceps):
- Pull-Ups
- Bent Over Rows
- Bicep Curls
- Deadlifts
- Day 3 (Legs):
- Squats
- Lunges
- Leg Press
- Calf Raises
- Day 4 (Shoulders and Core):
- Shoulder Press
- Lateral Raises
- Planks
- Russian Twists
The bench press is more than just an exercise; it’s a fundamental component of any strength training program aimed at building a robust upper body. By mastering proper technique, avoiding common pitfalls, and incorporating variations, you can maximize your gains and achieve impressive results. Remember to listen to your body, progress at a safe pace, and enjoy the journey towards becoming stronger and fitter with each lift!